Connect-MgGraph (Microsoft Graph)
Connect to Microsoft Graph PowerShell using Connect-MgGraph cmdlet with appropriate permission scopes. Authenticate with user credentials, certificate-based authentication, or access tokens. Specify TenantId for multi-tenant scenarios and configure context scope for session management.
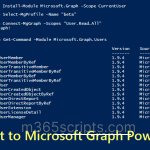
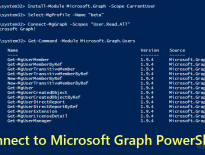
The Connect-MgGraph cmdlet is used to connect to Microsoft Graph PowerShell. You must install Microsoft Graph PowerShell SDK to use this cmdlet.
Else, you will receive the error: “The term ‘Connect-MgGraph’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable Program”
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
Connect-MgGraph [-Scopes] <string []>] [-TenantId] <string>] [-ForceRefresh] [-ClientId <string>] [-ContextScope {Process | CurrentUser}] [-Environment <string>] [-UseDeviceAuthentication] [-ClientTimeout <double>] [-Break] [<CommonParameters>] |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
Connect-MgGraph [-ClientId] <string> [-CertificateName] <string>] [-CertificateThumbprint] <string>] [-Certificate <X509Certificate2>] [-TenantId <string>] [-ForceRefresh] [-ContextScope {Process | CurrentUser}] [-Environment <string>] [-ClientTimeout <double>] [-Break] [<CommonParameters>] |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Connect-MgGraph [-AccessToken] <string>] [-Environment <string>] [-ClientTimeout <double>] [-Break] [<CommonParameters>] |
The ‘Connect-MgGraph’ cmdlet initiates connection to Microsoft Graph. After successful connection, you will receive “Welcome to Microsoft Graph!” message.
Example 1: Initiate a connection.
|
1 |
Connect-MgGraph –Scopes "User.Read.All" |
This command connects Microsoft Graph with “User.Read.All” permission scope. Each Graph API requires different scope permission. To identify the required scope, you can refer to the Microsoft doc.
Example 2: Connect Microsoft Graph with Tenant id
|
1 |
Connect-MgGraph – TenantId “436r2398-87e4-34y8-43r3h4drf78" |
If you don’t specify the TenantId parameter, it will create a session with the last tenant you signed in.
-Access Token <string>
Specifies a bearer token for Microsoft Graph service. Access tokens do timeout and you’ll have to handle their refresh.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? 1 Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AccessTokenParameterSet Aliases None Dynamic? false |
-Break
Wait for .NET debugger to attach.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? Named Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name (All) Aliases None Dynamic? false |
-Certificate <X509Certificate2>
The Certificate parameter specifies the certificate that’s used for Certificate-based authentication (CBA). An X.509 certificate supplied during invocation.
Don’t use this parameter with the CertificateThumbprint parameter.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? Named Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AppParameterSet Aliases None Dynamic? false |
-CertificateName <string>
The name of your certificate. The Certificate will be retrieved from the current user’s certificate store.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? 2 Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AppParameterSet Aliases CertificateSubject Dynamic? false |
-CertificateThumbprint <string>
Specifies the certificate thumbprint of a digital public key X.509 certificate of a user account that has permission to perform this action. For example, 83213AEAC56D61C97AEE5C1528F4AC5EBA7321C1.
Don’t use this parameter with the Certificate parameter.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? 3 Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AppParameterSet Aliases None Dynamic? false |
-ClientId <string>
The client id of your application.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? true Position? 1 Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AppParameterSet, UserParameterSet Aliases AppId Dynamic? false |
-Scopes <string []>
An array of delegated permissions to consent to.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? 1 Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name UserParameterSet Aliases None Dynamic? false |
-TenantId <string>
Specifies the ID of a tenant.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? Named Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name AppParameterSet, UserParameterSet Aliases Audience Dynamic? false |
-UseDeviceAuthentication
Use device code authentication instead of browser control
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
Required? false Position? Named Accept pipeline input? false Parameter set name UserParameterSet Aliases DeviceCode, DeviceAuth, Device Dynamic? false |